Describe the Basic Steps of a Hadley/ferrel/polar Cell
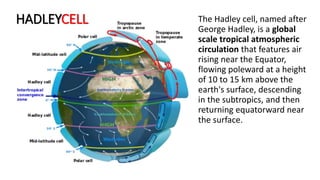
Thermally Direct Cells Hadley and Polar Cells Both cells have their rising branches over warm temperature zones and sinking braches over the cold temperature zone. Along the equator strong solar heating causes air to expand upward and diverge toward the poles to about 25-degrees latitude where it sinks and returns to the equator at low levels.
As Geography Atmosphere And Weather Atmospheric Circulation Model
The Polar cell At the poles air is cooled and sinks towards the ground forming high pressure this known as the Polar high.

. In the Ferrel cell air flows poleward and eastward near the surface and equatorward and westward at higher altitudes. The polar front forms where these two contrasting air mass meet leading to ascending air and low pressure at the surface often around the latitude of the UK. These Ferrel cells Hadley Cell and polar cell set the configuration for the general circulation of the atmosphere.
The general circulation is virtually synonymous with the large-scale circulation although the former is sometimes taken to be the time- or ensemble-averaged flow. This movement is the reverse of the airflow in the Hadley cell. This cell is called the polar cell.
Warm moist air from the tropics gets fed north by the surface winds of the Ferrel cell. Ekman Layer frictional force Coriolis. All Articles Atmosphere Climate Weather.
In the Ferrel cell air flows poleward and eastward near the surface and equatorward and westward at higher altitudes. Jin-Yi Yu Step 2. Global Wind Patterns Describe the basic steps of a hadleyferrelpolar cell.
Terms in this set 5 Hadley cell. It then flows towards the lower latitudes. The Mid-latitude Ferrell cells are the most unstable and experience the most windy conditions.
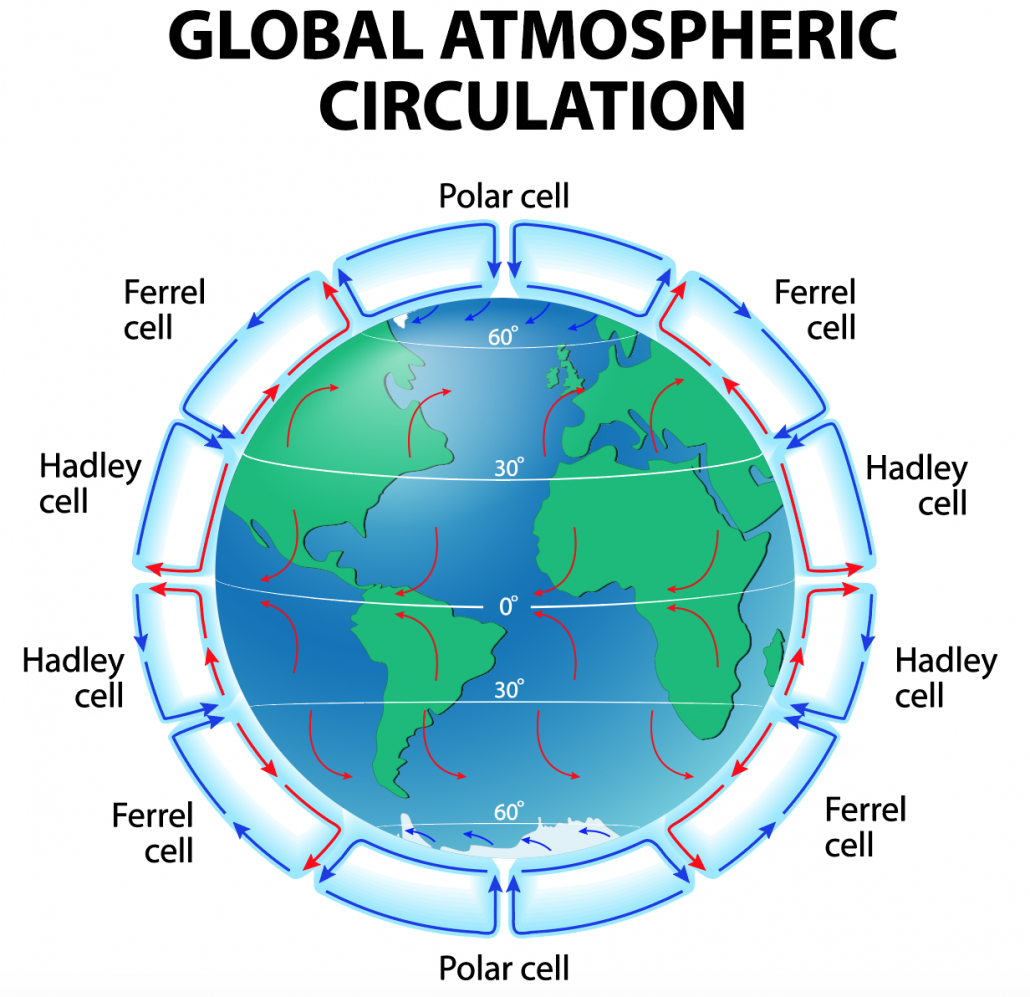
The Polar cell is made up of frigid air due to low solar heating and is therefore denser. The Ferrel cells are indirect cells driven by the direct cells to the north and south of them. Properties of the Three Cells-Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell-Warmer at Equator ---- Cooler at polar region Is the Three-Cell Model Realistic-Yes the three-cell model explains reasonable well the surface wind distribution in the atmosphere-No the three-cell model can not explain the circulation pattern in the upper troposphere New Understanding of Cyclone after WWII.
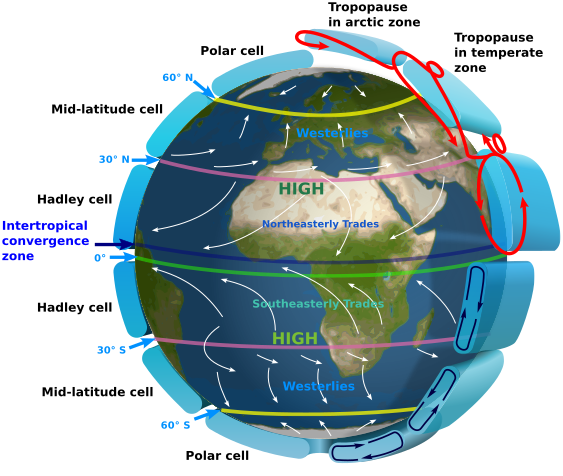
Their exact location wanders throughout the course of the year. In the Hadley cell air rises up into the atmosphere at or near the equator flows toward the poles above the surface of the Earth returns to the Earths surface in the subtropics and flows back towards the equator. Jin-Yi Yu Winds and Surface Currents Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell Figure from The Earth System ESS5 Prof.
Air in contact with the hot land is warmed and rises forming the the permanent equatorial low pressure belts Doldrums Trade winds are blown into this low pressure belt and meet at the ITCZ. The Ferrel cell however is still not a good representation of reality because it. Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air through the atmosphere categorized into the Hadley Ferrel and Polar.
The warm air rises creating a band of low pressure at the equator. Blow toward the equator. Atmospheric Circulation and Weather System doorsteplearninggeography climatologyhumidity and types of humidity - httpsyoutubeY4HNCR8lNP4Hadley Cell.
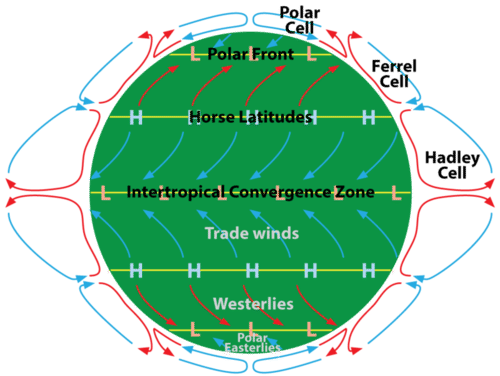
Equatorial low or intertropical convergence zone ITCZ region of low air pressure at the surface found along the equator associated with Hadley cell trade winds. Explain why deserts form predictably at 30 o NS latitude. Ferrels model was the first to account for the westerly winds between latitudes 35 and 60 in both hemispheres.
The circulation within the Ferrel cell is complicated by a return flow of air at high altitudes towards the tropics where it joins sinking air from the Hadley cell. Explain why so much precipitation occurs near the equator. Both cells directly convert thermal energy to kinetic energy.
THE LARGE-SCALE CIRCULATION OF THE ATMOSPHERE is normally taken to mean the flow on scales of the weather several hundred or a thousand kilometres say to the global scale. Identify the location on earth where the solar radiation is most direct. At polar latitudes the cold dense air subsides near the poles and blows towards middle latitudes as the polar easterlies.
Together the Hadley Ferrel and polar cells comprise the three-cell model shown in the diagram. The Hadley cells converge at the equator to form the Intertropical Convergence Zone. Moist airwarmed in the ITCZ rises in strong convection currents.
The Ferrel Cell plays a major part in the poleward energy mainly heat transport. Thermally Indirect Cell Ferrel Cell This cell rises over cold temperature zone and sinks over warm temperature zone. Find an answer to your question The Hadley Ferrel and polar cells are all patterns of moonliteprincess29 moonliteprincess29 07252016 Biology High School answered The Hadley Ferrel and polar cells are all patterns of 1 See answer Advertisement.
The Hadley cells and polar cells are direct cells driven by convection and the subsidence of cold dense air. The Ferrel cell moves in the opposite direction to the two other cells Hadley. Surface Winds Figure from Oceanography by Tom Garrison ESS5 Prof.
This movement is the reverse of the airflow in the Hadley cell. This then meets cool dry air moving south in the Polar cell. Identify the direction the wind blows between.
This flow of air occurs because the Sun heats air at the Earths surface near the equator.
What Is The Tri Cellular Model Of Atmospheric Circulation Quora

Atmospheric Circulation Meteoblue

Geographybhai General Knowledge Current Affairs

Atmospheric Convection Convection Cells What Is A Convection Cell Study Com

Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell Abcd Xxx
What Is Global Atmospheric Circulation Internet Geography

Atmospheric Circulation Meteoblue
Circulation In The Atmosphere Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation

Global Atmospheric Circulation Polar Ferrel And Hadley Cells Flashcards Quizlet

General Circulation Of The Atmosphere

Hadley Cell An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Chapter 11 General Circulation Atmospheric Processes And Phenomenon

Atmospheric Circulation 1 Diagram Quizlet
What Is The Tri Cellular Model Of Atmospheric Circulation Quora

Atmospheric Circulation Mr Gray S History Emporium

Learn About Global Atmospheric Circulation Encounter Edu
Chapter 11 General Circulation Atmospheric Processes And Phenomenon
Comments
Post a Comment